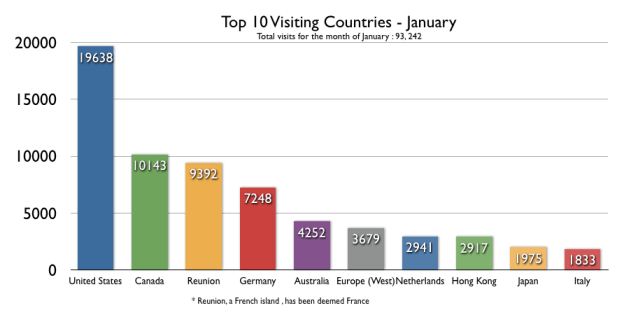
In response to my post yesterday one reader sent me a very thoughtful commentary that included this line at the end:
“Rather than compare [Freedom of Information] FOI legislation and Open Gov Data as if it’s “one or the other”, do you think there’s a way of talking about how the two might converge?”
One small detail:
So before diving in to the meat let me start by saying I don’t believe anything in yesterday’s post claimed open data was better or worse than Freedom of Information (FOI often referred to in Canada as Access to Information or ATI). Seeing FOI and open data as competing suggests they are similar tools. While they have similar goals – improving access – and there may be some overlap, I increasingly see them as fundamentally different tools. This is also why I don’t see an opportunity for convergence in the short term (more on that below). I do, however, believe open data and FOI processes can be complimentary. Indeed, I’m hopeful open data can alleviate some of the burden placed on FOI system which are often slow. Indeed, in Canada, government departments regularly violate rules around disclosure deadlines. If anything, this complimentary nature was the implicit point in yesterday’s post (which I could have made more explicit).
The Problem with Convergence:
As mentioned above, the overarching goals of open data and FOI systems are similar – to enable citizens to access government information – but the two initiatives are grounded in fundamentally different approaches to dealing with government information. From my view FOI has become a system of case by case review while open data is seeking to engage in an approach of “pre-clearance.”
Part of this has to do with what each system is reacting to. FOI was born, in part, out of a reaction to scandals in the mid 20th century which fostered public support for a right to access government information.
FOI has become a powerful tool for accessing government information. But the infrastructure created to manage it has also had some perverse effects. In some ways FOI has, paradoxically made it harder to gain access to government information. I remember talking to a group of retired reporters who talk about how it was easier to gain access to documents in a pre-FOI era since there were no guidelines and many public servants saw most documents as “public” anyways. The rules around disclosure today – thanks in part to FOI regimes – mean that governments can make closed the “default” setting for government information. In the United States the Ashcroft Memo serves as an excellent example of this problem. In this case the FOI legislation actually becomes a tool that helps governments withhold documents, rather than enable citizens to gain legitimate access.
But the bigger problem is that the process by which access to information requests are fulfilled is itself burdensome. While relevant and necessary for some types of information it is often overkill for others. And this is the niche that open data seeks to fill.
Let me pause to stress, I don’t share the above to disparage FOI. Quite the opposite. It is a critical and important tool and I’m not advocating for its end. Nor am I arguing the open data can – in the short or even medium term – solve the problems raised above.
This is why, over the short term, open data will remain a niche solution – a fact linked to its origins. Like FOI Open data has its roots in government transparency. However, it also evolved out of efforts to tear down antiquated intellectual property regimes to the facilitate sharing of data/information (particularly between organizations and governments). Thus the emphasis was not on case by case review of documents, but rather of clearing rights to categories of information, both created and to be created in the future. In other words, this is about granting access to the outputs of a system, not access to individual documents.
Another way of thinking about this is that open data initiatives seek to leverage the benefits of FOI while jettisoning its burdensome process. If a category of information can be pre-clear in advanced and in perpetuity for privacy, security and IP concerns then FOI processes – essential for individual documents and analysis – becomes unnecessary and one can reduce the transaction costs to citizens wishing to access the information.
Maybe, in the future, the scope of these open data initiatives could become broader, and I hope they will. Indeed there is, ample evidence to suggest that technology could be used to pre-clear or assess the sensitivity of any government document. An algorithm that assess a mixture of who the author is, the network of people who review it and a scan of the words would probably allow ascertain if a document could be released to an ATIP request in seconds, rather than weeks. It could at least give a risk profile and/or strip out privacy related information. These types of reforms would be much more disruptive (in the positive sense) to FOI legislation than open data.
But all that said, just getting the current focus of open data initiatives right would be a big accomplishment. And, even if such initiatives could be expanded, there are limits. I am not so naive to believe that government can be entirely open. Nor am I sure that would be an entirely good outcome. When trying to foster new ideas or assess how to balance competing interests in society, a private place to initiate and play with ideas may be essential. And despite the ruminations above, the limits of government IT systems means there will remain a lot of information – particularly non-data information like reports and analysis – that we won’t be able to “pre-clear- for sharing and downloading. Consequently an FOI regime – or something analogous – will continue to be necessary.
So rather than replace or converge with FOI systems, I hope open data will, for the short to medium term actually divert information out of the FOI, not because it competes, but because it offers a simpler and more efficient means of sharing (for both government and citizens) certain types of information. That said, open data initiatives offer none of the protections or rights of FOI and so this legislation will continue to serve as the fail safe mechanism should a government choose to stop sharing data. Moreover, FOI will continue to be a necessary tool for documents and information that – for all sorts of reasons (privacy, security, cabinet confidence, etc…) cannot fall under the rubric of an open data initiative. So convergence… not for now. But co-existence feels both likely and helpful for both.